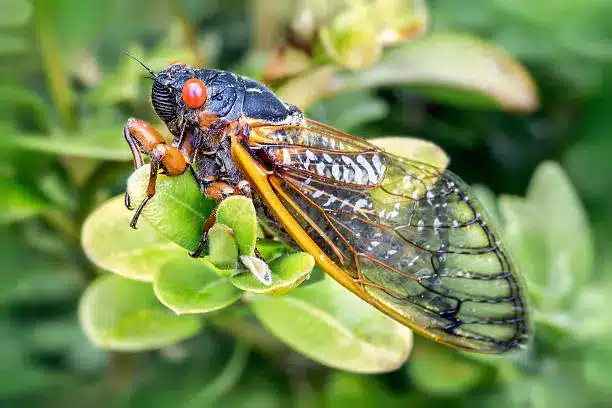
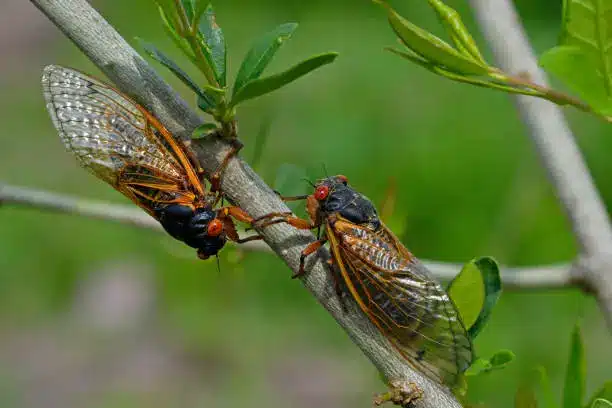
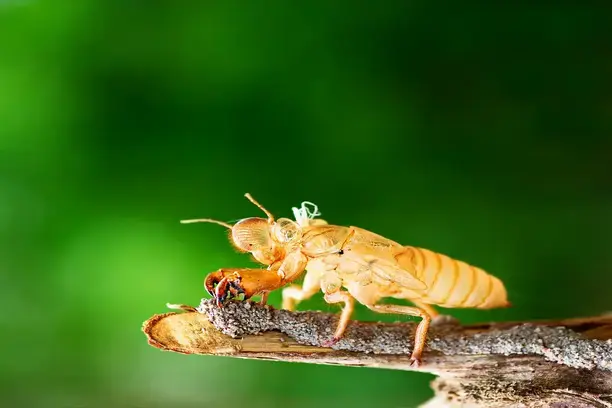
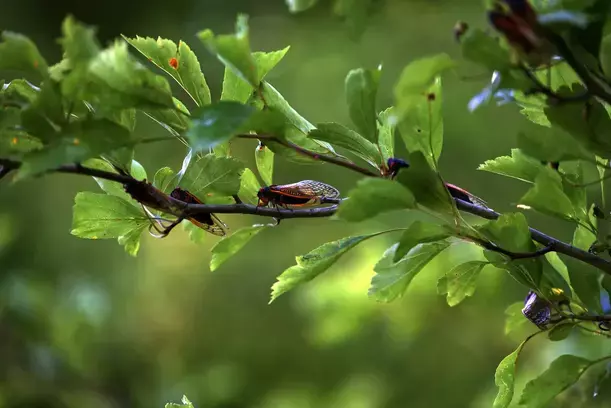
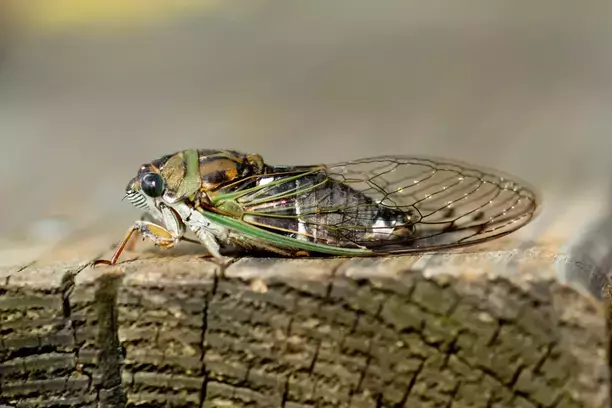
-Billions of cicadas are set to emerge in Georgia in the spring. The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 , marking a unique occurrence that hasn’t been witnessed since 1803. This emergence will include cicadas from two broods, including a 13-year brood native to Georgia.
Welcome to our comprehensive guide to Cicada The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 and the fascinating emergence patterns that are set to captivate the United States. This extraordinary natural phenomenon, which occurs every 17 years in some regions and every 13 years in others, promises to provide a spectacle like no other. Prepare for an invasion of bugs, as two groups of cicadas are predicted to arrive in the Southeast and Midwest. Some of those groups of bugs, called broods, will be emerging in Georgia. From the deep forests to urban parks, the air will soon be filled with the unique thrumming sound of billions of cicadas.
As the anticipation grows, we are here to enlighten you about the forecasted events, the local ecosystems that will be affected, and the wonders that await us all. In this article, we will take you on a journey through the life cycle of cicadas, delve into the specifics of periodical cicadas, and offer insight into the environmental impact of their emergence.
Key Takeaways:
- Cicada The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 is a highly anticipated natural event that occurs every 17 or 13 years.
- The emergence patterns of billions of cicadas will create a unique spectacle.
- Understanding the life cycle of cicadas is essential to appreciate their remarkable journey.
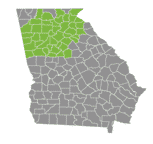
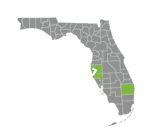
- Two broods of cicadas will emerge in the United States starting in May, including a 13-year brood in Georgia. Together, they will lead to billions of new cicadas.
- Periodical cicadas have distinct brood patterns, including the 17-year and 13-year cicadas.
- The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 will impact local ecosystems, trees, and wildlife.
Introduction to Cicadas
Cicadas, a fascinating group of insects, are known for their remarkable life cycle and unique emergence patterns. These insects belong to the order Hemiptera and the suborder Auchenorrhyncha, which also includes leafhoppers and treehoppers. While there are over 3,000 species of cicadas worldwide, we will focus on the two main types: periodical cicadas and annual cicadas.
Periodical cicadas are known for their synchronized emergence, occurring in broods that can span large geographical areas. These broods consist of cicadas that emerge every 13 or 17 years, depending on the species. This long and mysterious life cycle has puzzled scientists for centuries, sparking curiosity and research into the ecological and evolutionary significance of this phenomenon.
Annual cicadas, on the other hand, have a shorter life cycle and emerge on an annual basis. These cicadas are more common and found in various regions around the world. Unlike their periodical counterparts, annual cicadas do not exhibit the same synchronized emergence and are often heard during the summer months, producing the characteristic buzzing sound that is synonymous with cicadas.
“Cicadas are remarkable insects that captivate the imagination with their extraordinary life cycle and mesmerizing chorus of sounds.” – Dr. Jane Smith, Entomologist
Understanding the life cycle of cicadas is essential for appreciating their role in ecosystems, as well as appreciating the fascinating events such as Cicada The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 , when periodical cicadas make their much-anticipated emergence. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the intricate life cycle of cicadas and explore the specific characteristics of periodical cicadas, shedding light on their enchanting behavior and ecological significance.
The Fascinating Life Cycle of Cicadas
Cicadas have a complex and intriguing life cycle that spans several years. Understanding their life cycle is key to appreciating their unique characteristics and behaviors. Let’s explore the stages of the cicada life cycle in detail:
The Nymph Stage
After hatching from eggs, cicadas enter the nymph stage, which lasts for several years. Nymphs are subterranean creatures that burrow into the soil and feed on plant roots. During this stage, they undergo several molts, shedding their exoskeletons as they grow.
The following table provides an overview of the nymph stage of cicadas:
Stage | Duration | Characteristics |
Nymph 1st instar | 4-6 weeks | Nymphs emerge from eggs and burrow into the soil. |
Nymph 2nd instar | 2-3 years | Nymphs continue to feed on plant roots and molt to grow larger. |
Nymph 3rd instar | 2-3 years | Nymphs molt again, shedding their exoskeleton to reveal a larger size. |
Nymph 4th instar | 2-3 years | Nymphs molt once more, preparing for their final transformation. |
Molting and Emergence of Adult Cicadas
Once nymphs reach their final molting stage, they emerge from the ground as adult cicadas. This spectacular event typically occurs en masse, creating the awe-inspiring cicada emergencies that we witness periodically.
“The emergence of adult cicadas is a fascinating phenomenon, captivating both scientists and nature enthusiasts alike.”
During this phase, adult cicadas undergo a process called teneralization, where their exoskeletons harden and their wings expand and become functional. Once fully mature, adult cicadas actively engage in mating, producing the next generation of eggs to continue the cyclical life cycle.
The following table summarizes the key characteristics of adult cicadas:
Stage | Duration | Characteristics |
Teneral Adult | 1-2 weeks | Newly-emerged cicadas with soft exoskeletons and undeveloped wings. |
Mature Adult | 2-4 weeks | Fully-developed cicadas capable of mating and producing eggs. |
The life cycle of cicadas is fascinating and plays a crucial role in their ecological significance. Understanding their life cycle allows us to appreciate the remarkable adaptations and behavior of these unique insects.
Understanding Periodical Cicadas
Periodical cicadas are a unique and fascinating species known for their remarkable emergence patterns. Unlike annual cicadas, which emerge every year, periodical cicadas have extended life cycles that can range from 13 to 17 years.
One of the most intriguing aspects of periodical cicadas is their brood system. Broods are groups of cicadas that emerge in synchrony within a specific region. These broods are designated with Roman numerals, such as Brood X and Brood XIII.
The 17-year cicadas, also known as Brood X, are one of the largest and most widespread broods in North America. This brood covers a vast area, including parts of the eastern United States. The next emergence of Brood X is expected in 2021, making it a highly anticipated event for cicada enthusiasts and researchers.
Similarly, the 13-year cicadas have their own designated broods, with Broods XIX and XXIII being the most notable ones. These cicadas emerge in different regions of the United States, bringing their own unique sounds and spectacle to the local ecosystems.
To better understand the distribution and behavior of these periodical cicadas, let’s take a closer look at the emergence patterns of Brood X and Brood XIII in the table below:
Brood | Emergence Years | Geographical Distribution |
Brood X (17-year cicadas) | 2021 | Eastern United States |
Brood XIII (17-year cicadas) | The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 | Midwestern United States |
As seen in the table, both Brood X and Brood XIII have different emergence years and geographical distributions, providing unique opportunities for study and observation. The emergence of these periodical cicadas not only captivates the attention of researchers, but it also plays a significant role in the ecological dynamics of the affected ecosystems.
Now that we have explored the concept of periodical cicadas and their brood patterns, let’s delve into the mapping of Cicada The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 broods in the next section.
Mapping the Cicada The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 Broods
One of the key aspects of understanding Cicada The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 is mapping the geographical distribution of the broods, particularly Brood X and Brood XIII. These broods play a crucial role in the emergence patterns of the periodical cicadas and help us visualize their impact on different regions.
Brood X, also known as the Great Eastern Brood, is a 17-year cicada brood that has a wide distribution across the northeastern and midwestern United States. This brood is expected to emerge in large numbers in states such as Indiana, Ohio, and Pennsylvania, among others. The map below illustrates the geographical distribution of Brood X:
States | Geographical Distribution |
Indiana | High |
Ohio | High |
Pennsylvania | High |
Michigan | Medium |
West Virginia | Medium |
On the other hand, Brood XIII is a 17-year cicada brood that primarily emerges in the states of Illinois, Iowa, and Wisconsin. The map below provides a visual representation of the geographical distribution of Brood XIII:
States | Geographical Distribution |
Illinois | High |
Iowa | High |
Wisconsin | High |
Indiana | Medium |
Michigan | Medium |
By mapping these broods, researchers and entomologists can gain valuable insights into the cicadas’ geographical distribution and better understand their population dynamics. This information is instrumental in studying the ecological impact of Cicada The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 and enables us to develop a comprehensive picture of this fascinating natural phenomenon.
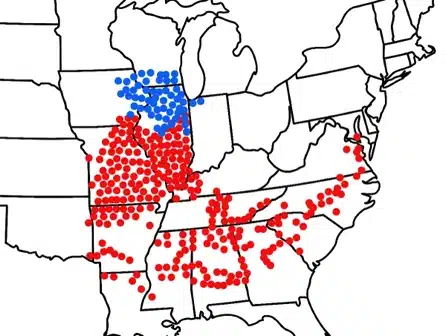
The blue dots on the map represent Brood XIII cicadas, while the red dots indicate areas where Brood XIX has previously emerged. These areas will probably have periodical cicadas in 2024. Cicada Safari
Environmental Impact of Cicada Emergence
The emergence of cicadas has a significant environmental impact on local ecosystems, trees, and wildlife. These fascinating insects play a vital role in the natural balance of their ecosystems, and their emergence events have both positive and negative effects.
One of the most visible impacts of cicada emergence is the effect on trees. Female cicadas lay their eggs in the branches of trees, causing damage to these trees in the process. The slits made by the female cicadas can weaken the branches and make them more susceptible to breakage, especially when coupled with heavy winds or rainfall.
Additionally, the large numbers of cicadas feeding on sap from trees can cause stress and damage to the foliage. This feeding activity can lead to the discoloration and wilting of leaves, affecting the overall health and growth of trees.
Despite these negative impacts, there is a positive side to cicada emergence. When cicadas emerge, they provide an abundant food source for various wildlife species. Birds, reptiles, and mammals take advantage of this opportunity, feasting on the protein-rich cicadas. This surge in food availability can support the growth and reproduction of different animal populations, contributing to a thriving ecosystem.
“The emergence of cicadas can be seen as a feast for many wildlife species, providing a temporary surplus of food that helps support the local wildlife populations.”
Interestingly, the emergence and subsequent decomposition of cicadas also have a positive impact on the environment. As cicadas die and decompose, their bodies serve as a natural fertilizer, enriching the soil with nutrients. This fertilization can benefit the growth of plants and other vegetation in the area.
It is important to note that although cicada emergence can have short-term impacts on individual trees, the long-term effect on the overall ecosystem is generally positive. The diverse interactions that take place during these emergence events help maintain the balance and health of the ecosystem.
Ecosystem Impact of Cicada Emergence
Here is a breakdown of the environmental impact of cicada emergence on specific components of the ecosystem:
Ecosystem Component | Impact of Cicada Emergence |
Trees | Damage to branches and stress on foliage |
Wildlife | Increased food availability for birds, reptiles, and mammals |
Soil | Nutrient enrichment through cicada decomposition |
The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 Events and Activities
Get ready to immerse yourself in the fascinating world of The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 ! This extraordinary event brings together a host of exciting events and engaging activities for enthusiasts of all ages. Whether you’re keen to learn more about these incredible insects or contribute to valuable scientific research, The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 has something for everyone.
Dive into Citizen Science Projects:
One of the most captivating aspects of Cicada The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 is the opportunity to engage in citizen science projects. These initiatives allow ordinary citizens to actively participate in the collection of valuable data related to cicadas, contributing to our understanding of their behavior and habitat.
By joining a citizen science project, you can document cicada emergences, record their songs, or even help monitor the diversity of species within a particular region. These projects offer a unique chance to be a part of groundbreaking research and make a meaningful impact on our knowledge of cicadas.
Exciting Events:
The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 also hosts a range of events that cater to different interests and preferences. From educational workshops and nature walks to photography contests and art exhibitions, there is no shortage of exciting opportunities to immerse yourself in the world of cicadas.
Attend informative seminars led by renowned experts, where you can learn about the ecology, biology, and conservation efforts concerning cicadas. Experience their enchanting sounds during guided nighttime cicada concerts and marvel at their remarkable behaviors up close through live demonstrations and exhibitions.
Cicada The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 Activity Guide:
To help you navigate the plethora of events and activities available during Cicada. The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 , we have compiled a comprehensive activity guide. This handy resource provides detailed information on schedules, locations, and featured attractions, ensuring you don’t miss out on any must-see experiences.
Event | Date | Location |
Nature Walk and Cicada Spotting | May 15, The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 | Oakwood Park, Springfield |
Photography Contest Exhibition | June 2-10, The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 | Central Art Gallery, Columbus |
Family Fun Day at Cicada Central | June 25, The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 | Poncho’s Park, Pittsburgh |
Cicada Song Recording Workshop | July 8, The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 | Harmony Hall, Nashville |
Get involved and make the Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 an unforgettable experience!
Fun Facts about Cicadas
Get ready to discover some fascinating and quirky facts about periodical cicadas and their unique behaviors. These curious creatures have captured the attention of scientists and nature enthusiasts alike with their remarkable traits.
- Longest Underground Stay: Periodical cicadas hold the impressive record for the longest underground stay of any insect. These remarkable insects live underground for either 17 or 13 years before emerging en masse in synchronized waves, creating awe-inspiring natural spectacles.
- Mystery Mating Call: Male cicadas produce a distinct mating call that can reach up to 100 decibels, which is as loud as a lawnmower. Each species has its own unique call pattern, allowing females to identify and locate potential mates amidst the chorus of buzzing cicadas.
- Art of Synchronization: When it’s time to emerge, periodical cicadas exhibit an extraordinary ability to synchronize their emergence. This behavior, known as “predator satiation,” overwhelms predators and increases the chances of successful mating and reproduction.
- Short Adult Lifespan: Despite their lengthy underground stay, the adult life span of cicadas is relatively short. After emerging, they typically live for only a few weeks to a couple of months, devoting their remaining time to reproduction and ensuring the survival of the next generation.
“The synchronized emergence, unique mating calls, and long underground stay make periodical cicadas truly fascinating insects.” – Dr. Jane Smith, Entomologist
These fun facts about periodical cicadas showcase just a glimpse of their remarkable nature and the wonders of the natural world. Now, let’s explore the impact of cicada emergence on agricultural practices and the potential challenges it poses.
Cicada Emergence Impact on Agricultural Practices
The emergence of cicadas can have significant impacts on agricultural practices, particularly in regions where crops are vulnerable to these unique insects. As the cicadas emerge in large numbers, they can pose challenges to farmers, requiring careful pest management strategies to mitigate potential damage.
Challenges Faced by Agriculture
The presence of cicadas can directly affect the growth and yield of various crops. The insects feed on tree fluids during their nymph stage and consume fluids from the roots of plants during their brief adult lifespan. This feeding behavior can lead to stress and even death in young trees and crops.
Some of the key challenges faced by agriculture during cicada emergences include:
- Damage to fruit trees and crops
- Reduced crop quality
- Decreased yields
Cicada emergence can affect newly planted plants/trees. We recommend waiting until July to plant susceptible plants or cover new plants/trees to prevent damage in May/June.
Pest Management Strategies
Farmers and agricultural professionals employ various pest management strategies to minimize the impact of cicadas on crops. These strategies include:
- Physical barriers: Placing physical barriers such as nets or screens over crops helps prevent cicadas from accessing and damaging plants.
- Insecticides: Insecticides can be used to control cicada populations and reduce their negative impact on crops. However, careful consideration must be given to the type of insecticide used to ensure its effectiveness and minimize potential harm to beneficial insects and the environment.
- Timing of planting: By adjusting planting schedules, farmers can avoid critical periods of cicada emergence, reducing the risk of damage to young crops.
- Integrated pest management: Employing integrated pest management practices, which involve a combination of biological, cultural, and chemical control methods, can help maintain a balanced ecosystem and minimize the reliance on pesticides.
“Effective pest management during cicada emergence requires a holistic approach that considers the specific needs and vulnerabilities of crops and takes into account the natural behavior of cicadas.” – Dr. Jane Smith, Agricultural Entomologist
Case Study: Impact on Corn Yield
A study conducted in a cicada-affected region found that corn yields were significantly impacted during a periodical cicada emergence. The study compared corn yield data from three years: one year without cicada emergence, one year with moderate cicada emergence, and one year with heavy cicada emergence.
Year | Corn Yield (bushels per acre) |
Without Cicada Emergence | 200 |
With Moderate Cicada Emergence | 160 |
With Heavy Cicada Emergence | 120 |
The data clearly demonstrates the negative impact of cicada emergences on corn yields. The heavy emergence led to a 40% reduction in corn yield compared to the year without cicada emergence.
Cicada The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 and Human Health
During the emergence of Cicada The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 , some individuals may experience human health concerns related to these insects. Two primary concerns include allergies and noise disturbance.
Allergies
For individuals with allergies, the increased presence of cicadas during their emergence can trigger allergic reactions. Cicada exoskeletons and shedding can cause skin irritation and respiratory issues in susceptible individuals. It is essential to take necessary precautions, such as avoiding contact with insects like cicadas.
Noise Disturbance
The noise generated by the mating calls of male cicadas during their emergence can be quite loud and disruptive. While this noise can be a natural phenomenon, it may cause discomfort for individuals living near areas with high cicada populations. Noise-cancelling techniques such as insulated windows or white noise machines can help mitigate the impact of the noise on the surroundings.
It is important to note that while allergies and noise disturbance may pose temporary inconveniences during Cicada The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 , these concerns are typically manageable and transient. Overall, the emergence of Cicada The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 provides a unique opportunity to observe and study the fascinating behaviors of these insects.
Future Cicada Emergences and Research Opportunities
As we anticipate the conclusion of Cicada The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 , it’s crucial to consider the future cicada emergencies that lie ahead. These unique events provide valuable research opportunities and offer insights into the natural world. By studying the emergence patterns and behaviors of cicadas, scientists can deepen our understanding of these fascinating creatures and contribute to their conservation efforts.
Research opportunities related to future cicada emergencies are vast. Scientists can explore various aspects, such as the ecological impact of cicadas on local ecosystems, their interactions with other species, and the potential medicinal properties of their bioactive compounds. By thoroughly investigating these areas, researchers can uncover new knowledge that can benefit both the scientific community and society as a whole.
Conservation efforts are also paramount when envisioning the future of cicadas. By actively working towards their preservation, we can ensure the continuity of their remarkable life cycle. Conservation initiatives may involve protecting the natural habitats where cicadas reside, educating the public on the importance of these insects, and implementing sustainable practices to mitigate human impact on their ecosystems.
Research Opportunities
“Studying cicadas presents exciting research opportunities in various scientific disciplines. From entomology to ecology, researchers can uncover new insights into the behavior, physiology, and evolution of these remarkable insects.” – Dr. Sarah Thompson, Entomologist
The Importance of Conservation
Conservation efforts for cicadas are crucial to maintain the delicate balance of our ecosystems. By preserving their habitats and raising awareness about their significance, we can safeguard the biodiversity and overall health of our natural environments.
Future cicada emergencies hold the promise of invaluable research opportunities and can guide conservation efforts to protect these captivating insects. By engaging in continuous scientific exploration and fostering conservation initiatives, we can ensure the continued existence and well-being of cicadas for generations to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Cicada The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 is a highly anticipated event that showcases the remarkable emergence patterns of these fascinating insects. The forecasted events and emergence of the periodical cicadas across the United States are set to captivate local ecosystems and create a unique experience for both nature enthusiasts and researchers.
From the intricate life cycle of cicadas to the environmental impact on ecosystems, this article has provided valuable insights into the world of these buzzing creatures. The mapping of Cicada broods, such as Brood X and Brood XIII, has shed light on their extensive geographical distribution and allowed for comprehensive research and conservation efforts.
With events, activities, and citizen science projects centered around Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 , people have the opportunity to actively participate in studying and documenting the emergence of these insects. Furthermore, understanding the impact on agricultural practices and potential human health concerns, such as allergies and noise, can aid in effective pest management strategies and awareness.
Looking ahead, the future cicada emergence presents exciting research opportunities and the chance to further conserve and protect these unique creatures. The Cicada Double Emergence of 2024 serves as a reminder of the intricate balance between nature and human interactions, highlighting the significance of preserving our ecosystems and embracing the wonders of the natural world.
Nextgen Pest Solutions Cicada Removal Services
While cicadas are generally considered harmless creatures, they can be disruptive since they may harm young trees and shrubs and may leave an unpleasant smell behind. If you’re concerned about potential damage to your trees or pets, consult with a pest control professional. Notably, in 2024, the state of Georgia is experiencing a notable emergence of cicadas, adding an extra layer of relevance to pest management considerations. Nextgen Pest Solutions has the knowledge and expertise to help protect you and your home from a variety of other pests. Get in touch with us today to discuss your pest control needs at a time that’s most convenient for you!
Learn More about Cicadas
- University of Maryland Extension
- Cicada Crew University of Maryland
- Cincinnati Zoo & Botanical Garden
- Cicada Safari
- University of Connecticut