Flea Bites
Fleas are blood sucking parasites that survive on human as well as animal blood. There are multiple species of fleas that are closely associated with humans and pets, but the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis) is the most common. Other species of fleas found in the United States include, the dog flea, the ground squirrel flea, and the Oriental rat flea. Despite the confusing names, the cat flea is most commonly found on pets, including dogs, but some animals in the wild are found carrying multiple species of fleas on their bodies at once. They have a remarkable ability to jump substantial heights, allowing them to move between hosts easily. Fleas are commonly found on animals like dogs and cats, as they are attracted to fur and require blood meals to reproduce. By attaching themselves to pets while they are outdoors or encountering infested animals, fleas can be transported into homes. Additionally, fleas often lurk in shaded areas like under trees, kennels, or dog houses, waiting for new hosts to pass by. Their mode of transportation and preference for blood-feeding on animals contribute to the widespread distribution and infestation of fleas.
Fleas are small, an adult measures around 1/16 of an inch, reddish-brown, and wingless. Fleas are an irregular shape; they appear as if they were squished from both sides of their body. Fleas do not fly, but their powerful legs are well-adapted for jumping. Their flat bodies allow them to easily navigate through the hairs on their host’s body. The flea’s body is hard and shiny and covered with many hairs and spines which point towards the back. Under a microscope you can clearly see a robust mustache on the flea’s face. This distinctive mustache of spiny hairs helps to anchor the flea to its host. Fleas have specially adapted sucking mouthparts, which allows them to pierce through fur and skin and draw up blood from mammals.
Fleas have plagued animals and humans for millennia. Fleas are not a species specific ectoparasite, meaning they will attack humans, dogs, cats, birds, rats, squirrels, chickens, rabbits, and many other mammals. Fleas prefer animals, but if given the opportunity they will certainly bite humans. However, most fleas have a difficult time completing their life cycle on humans in a modern home. Usually, if fleas are present in a home, animals are also present somewhere. If the homeowner has no pets, a hidden infestation of rodents, raccoons, or other wildlife is very likely.
Why Do Fleas Bite?
In short, fleas bite because they require a blood meal to complete their life cycle. Fleas go through complete metamorphosis, egg, pupa, larvae, and adult. Fleas most commonly infest homes where pets are present, but not always. Flea “hot spots” mirror the patterns of their hosts. Fleas will be most likely concentrated in areas of pet bedding or resting places. If a flea infested pet sleeps on your recliner or in your bed, there will likely be all life stages of fleas found in those areas.
A female flea loosely lays tiny, white, oval shaped eggs on the hairs of the host or in areas where the host spends a lot of time, such as pet bedding. Approximately 18 days later, the eggs hatch and wormlike larvae emerge. The flea larva mainly eats adult flea feces, but may feed on other organic matter, such as hair or dead skin cells. The flea larvae spins a cocoon and pupates. It then emerges as an adult flea in search of a blood meal. In order for this life cycle to continue, the flea must partake in a blood meal. Contrary to belief, fleas cannot go through several generations without having a blood meal. The most difficult part of this lifecycle for the flea is for there to be enough food for the larvae to survive. Frequent vacuuming of floors, under furniture, couches (even under cushions), and other places where hair, skin, and adult flea feces accumulate will greatly slow down an infestation.
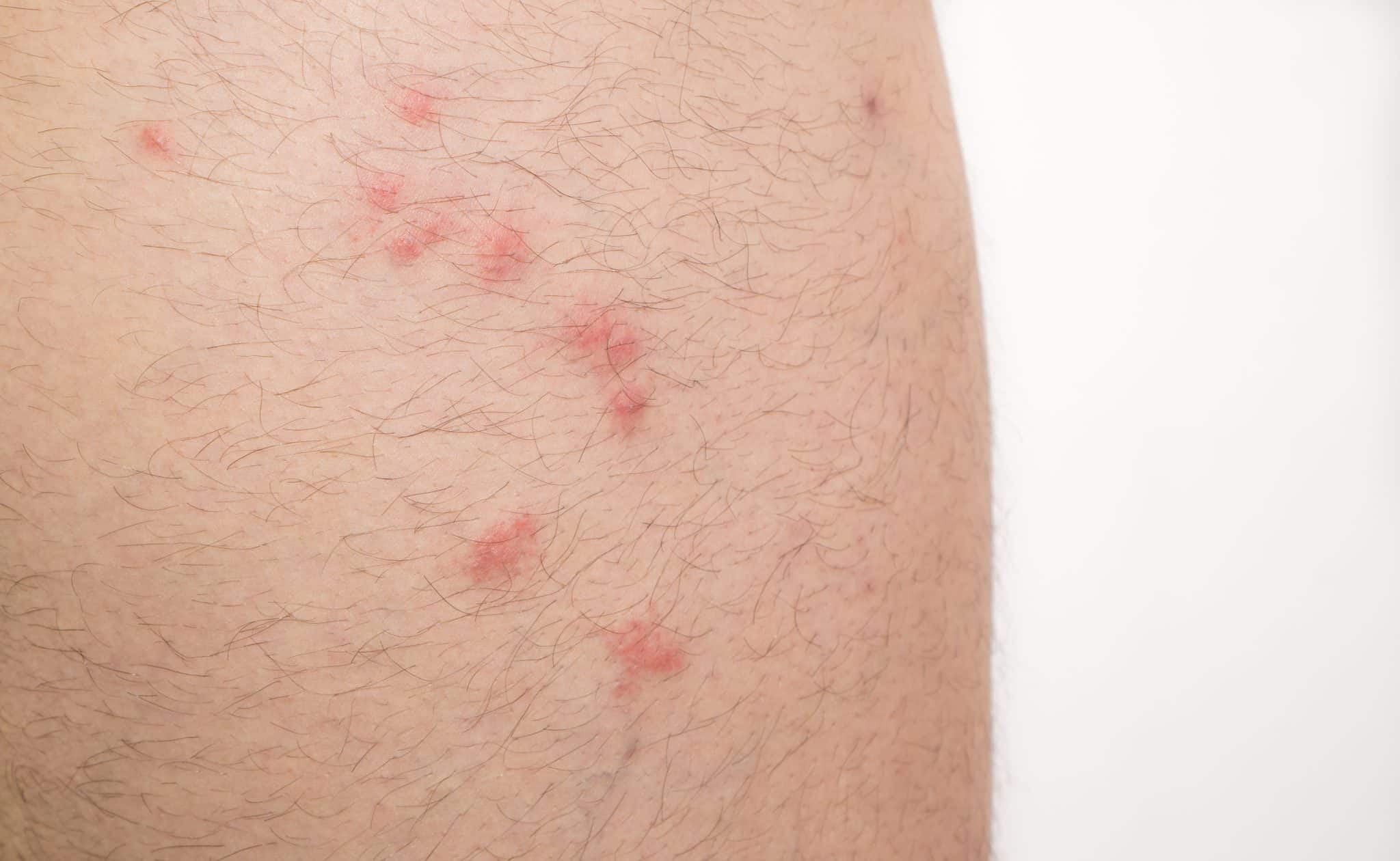
What Do Flea Bites Look Like on Humans Leg?
Cat fleas do not live on humans, but they will certainly bite humans. Fleas locate their host by sensing body heat, carbon dioxide that we exhale, movement, and vibration. Fleas have strong legs that they use to jump onto their host and powerful claws that they use to hold onto your skin. Their mouthparts have a needle-like projection called a proboscis. This proboscis pierces your skin and draws blood from your body into the flea’s mouth. Upon this action, flea saliva enters your bloodstream which triggers a reaction in most people.
Flea bites on humans are usually concentrated on the lower extremities of the body. Fleas rest in carpeting, or on pet’s bedding which is likely on the floor, therefore your feet, ankles, and lower legs are within their jumping range. Of course, flea bites are not ALWAYS on these areas. If fleas are brought to your bed by your pet, your flea bite, or even a bedbug bite, could be anywhere within jumping distance. If fleas are resting in your recliner, they may bite you on your abdomen or arms. Fleas will bite you wherever they can reach you, but most commonly it is around the feet and ankles.
Flea bites are usually accumulated in clusters with little to no rhyme or reason. There is no pattern or design to flea bite clusters. After a flea bites you, a small bright red bump forms on your skin. A small reddish halo may emanate from the centered red pustule. Unlike mosquito bites that may swell over time, flea bites do not usually swell up over time.
As stated above, fleas truly prefer to feed on our pets rather than humans. Therefore, excessive flea bites on humans is not as common as you would imagine. As with all bug bites, a person’s individual reaction to flea bites will vary. Some people may not have a visible skin reaction at all, while others exhibit a more severe allergic reaction. When flea saliva is injected into our body, every human has a different immune response. Most people react with an itchy red bump, but others may react with an itchy red bump and hives over the general area.
The most common scenario of fleas biting humans is when a pet dies or a tenant with pets moves out. The fleas remain but no longer have their favorite food source. They resort to biting the humans in the home. This often happens to new tenants in apartment buildings.
Flea Bite vs. Bed Bug Bite
The most decisive method of differentiating between a flea bite and a bed bug bite is finding the bug itself. Bed bugs establish themselves in cracks or crevices in or near the bed. Bedbugs are rarely found on their host. Similarly, fleas are usually concentrated on their host or around their main host’s bedding. Fleas prefer to feed on your pet, so they will most likely be found in your pet’s resting area and bedding. Fleas do spend most of their time on their host so inspect any pets closely. Fleas jump on and off their hosts while bed bugs walk from their hiding places and bite exposed skin.
Unlike bed bugs, most people feel the bite of a flea. If you feel a sharp prick, usually near your ankle or foot, but don’t react quickly enough to catch the insect that bit you, it probably wasn’t a bed bug. Bed bugs anesthetize the wound so as not to awaken or disturb their host. Fleas do not have this ability. Fleas quickly attack, bite, and are often swatted off humans as quickly as possible, which is why it’s essential to treat flea bites promptly.
Of course, every person has an individualized reaction, but flea bites and bed bug bites do look similar. Symptoms may vary but around the bite, there can be redness, itchiness and swelling which can be relieved with an antihistamine. They both usually present as small red itchy pustules. They are usually accumulated in clusters. Flea bites are commonly found on the feet, ankles, and lower legs whereas bed bug bites may be found anywhere. Bed bugs usually bite skin that is exposed at night and in contact with the mattress. Flea bites may be smaller than bed bug bites and are often a brighter red color than bed bug bites.
Ultimately, if no insect specimen can be located, circumstantial evidence may yield clues as to what is biting you. If your pet is uncharacteristically scratching and biting himself, check for flea dirt or feces on his skin. As a bed bug infestation grows, shed exoskeletons and feces may be located in crevices and bed bug hiding places. A pest control professional is extensively trained to know where and how to look for clues to these insects. A professional inspection may be required to accurately identify the bug that’s biting.
Flea Bite vs. Mosquito Bites
Mosquito bites and flea bites may both be obtained while enjoying the great outdoors. Mosquitoes are most aggressive at dawn and dusk, but if conditions are right, they will attack at all hours. Differentiating between flea and mosquito bites is usually done in the moment because you feel the attack! Mosquitoes buzzing around your face then coming in for the kill bite will be the clearest indication of a mosquito bite. However, mosquito bites are not always that crystal clear. Mosquitoes inject a mild painkiller into your body when they pierce your skin. This may cause you to not notice a mosquito bite at night while you are sleeping. The mosquito bite itself is often painless, whereas flea bites tend to be mildly painful. Stepping into a dry sandy area and your ankles and legs inundated with small jumping fleas, indicate flea bites.
Mosquito bites and flea bites look different as well. Although both insects pierce your skin then suck your blood, a mosquito bite usually results in a larger red welt than a flea bite. In addition, mosquito bites sometimes spread out with time and turn more whiter in color as they progress. In most individuals, flea bites remain small and very bright red.
Chigger Bites vs. Flea Bites
Chiggers, often called red bugs, are the larval stage of a mite of the Trombiculidae family. Chiggers are actually arachnids, more closely related to spiders, scorpions, and ticks than fleas. However, when chiggers attack the skin, the spots they leave look remarkably similar to flea bites. Although humans are not ideal hosts for chiggers, they will readily bite humans.
Chiggers live outdoors in soil that is shaded by vegetation. Chiggers are a light red color and very small, only about 1/100 of an inch in length. Though they don’t suck blood they are considered parasitic. As you pass through their environment, fleas like to attach to clothing. They usually explore a host for several hours before deciding where to feed. They usually choose areas where clothes are tight on the skin or where the skin is thin. Chigger bites are common around the waist band, at the ankles where socks fit tightly, in the armpits, or groin area. Chiggers pierce your skin and inject a digestive enzyme. This enzyme disintegrates skin cells and dissolves tissue. They then suck up this liquefied tissue for nourishment. Itching, redness, and swelling usually begins 4-8 hours after the chiggers have begun their feeding.
On a wild animal, chiggers usually feed for about 3 days before they fall off. They rarely last this long on a human host. Bathing in hot soapy water is usually enough to disconnect the chigger. Although chiggers usually fall off of humans before you even notice the bites, sometimes a person’s body reacts by swelling around the chigger making it appear the chigger has burrowed into the skin. A common myth is that chiggers burrow under your skin and must be dug out. This is not true and attempting this, such as scratching the bite, may lead to a secondary infection. The bites are itchy, but one needs to resist the urge to scratch them. The chigger is long gone by this point in time.
The immune response to the digestive fluid that is injected during a chigger attack leaves aan itchy red welt similar to flea bites. Sometimes chigger bites develop white pustules or bumps atop the red swollen area. Itching and discomfort usually lasts for 24-48 hours after a chigger bite, but the redness may last for a week or more
Sand Flea Bites
Colloquial language is a funny thing, and the term sand fleas is no exception. What many people refer to as sand fleas are actually nothing more than a common flea that is breeding in the sand or soil outside. Our common fleas can live and breed both indoors and outdoors, and symptoms of flea bites include itchiness and redness. Fleas prefer outdoor areas with plenty of shade and moisture. Avoid overwatering and keep your yard mowed and trees and shrubs trimmed. Remember that fleas often travel on rodents. Keeping your yard and home rodent free with a preventative rodent program will help to reduce the number of fleas in your yard. Completely eliminating fleas outdoors is nearly impossible, but by modifications to the environment and targeted insecticide use, a reduction in their population is possible.
Although not a concern here in the United States another insect that is often referred to as a sand flea is the parasitic chigo flea or Tunga penetrans. This flea is commonly called a jigger, sand flea, or chigo and is located in some areas of the Caribbean, equatorial Africa, Central and South America, and India and Pakistan. This flea causes the disease Tungiasis in humans when pregnant chigo fleas burrow into the feet of humans. A gravid female claws her way into the foot with her back end extending out about 1 cm. She continues to feed and shed eggs for about 2 weeks. When a chigo flea is attached and engorged, the host will experience inflammation and redness, itching and irritation, and serious secondary infections are common.
In some areas of the Southern United States, “sand flea” is also used to refer to biting midges which are also commonly called “no-see-ums”. These small gnats are actually a type of fly and not a flea at all. Despite the name, they are visible. They probably acquired the name “sand flea” because they are about the same size and shape as a flea, have a sharp/painful bite, and are most commonly found in coastal sandy areas. These “sand fleas” often leave a small red mark and itchiness that can last for several days. As with true fleas, this reaction will vary from person to person.
To make matters more complicated, some of the best fishing baits found on the beach are referred to as sand fleas. Florida fishermen go to great lengths to secure these arthropods to use as bait for red drum, pompano, sheepshead, and redfish. These sand fleas are caught with a rake-like instrument with a basket. Forging into the waves with this apparatus, fishermen scoop up a pile of beach sand in the surf, sift through the sand, and occasionally come up with a “sand flea.” These sand fleas are small ocean crustaceans, not insects. Like a flea, they appear to hop around, and are often referred to as beach fleas, sand hoppers, or beach hoppers. The bait sand flea does not bite humans, but larger fish surely will take a bite out of a sand flea.
Symptoms of Flea Bites
The most prolific symptom of flea bites is red itchy pustules. The center of this red eruption is where the flea inserted its mouthpart into your skin. Often redness extends out from the center as a halo effect. There is usually little to no swelling in the halo portion of the flea bite. Because they are usually nesting and breeding close to the ground, humans usually experience flea bites on the feet, ankles, and lower legs. Of course, never put nature in a box. Flea bites can occur any place that fleas can access. The common cat flea, which infests dogs, cats, and other mammals, often complete their life cycle on or very near their host. But fleas do not usually live on humans. They jump on for a quick bite, then jump back off to seek better living conditions. However, if your home or yard has a severe flea infestation, the quantity of bites can be numerous.
Unlike bed bug bites, which are usually not felt at the moment, a flea bite is usually immediately noticed. Whether the flea attack happened while walking through a sandy area outdoors, or while walking on your living room carpet, the piercing stab of the flea proboscis is sharp and painful. The red reaction that occurs is an allergic or histamine response from the flea’s saliva. Every person experiences differing levels of symptoms to flea bites. If you have fleas in your home, take immediate steps to get rid of them to stop the flea bites for both yourself and your beloved pet.
If you are experiencing itchy bites in bed but find no signs of bed bugs, fleas might be the culprit. Flea bites can cause similar symptoms and discomfort. To address flea bites, wash the affected area, use antiseptic, apply an ice pack to reduce itching, avoid scratching the bites, consider using lotions to alleviate the itch, and consult a pharmacist for antihistamines if needed. If the bites become infected or show signs of pus, it is crucial to contact your doctor promptly. It’s important to note that treating flea bites addresses the symptoms but does not solve the underlying infestation. To fully eradicate the problem, extermination methods must be employed alongside bite treatment to ensure the complete elimination of fleas.
When is Flea Season?
Fleas thrive in warm weather. In areas where Nextgen Pest Solutions operates, fleas are a year-round scourge. The Southeast region of the United States is the most welcoming and accommodating to fleas and their life cycle. The near constant heat and humidity allow for high rates of reproduction in the south. Even in cold snaps, flea eggs, larvae, and pupae do not necessarily die off. Depending upon temperature and other conditions, the flea life cycle can take between 2 weeks to 2 years. When it is cold or hosts are unavailable, the life cycle hits a pause button; eggs remain unhatched and pupae remain in their cocoon. Wherever you find yourself, the hottest driest months of the year will be peak flea season.
A “secondary” season may be apparent in the late fall or early winter. While not ideal conditions for the fleas themselves, this is often when wildlife (rodents, raccoons, etc) move into or under homes seeking a warm place to live during the cold weather. Often this is when homeowners take notice and we receive the most calls for flea treatments.
Flea Dirt
When you pull back your pet’s hair inspecting his skin, you may see black flecks that are not attached to anything. They are not moving and active, therefore not a flea, but lack the color variation of specks of dirt. This is likely flea fecal matter, also known as flea dirt. By carefully inspecting your pet, their bedding, your couch, or your carpets, you may find accumulations of this substance. Even if you are not finding live fleas, the presence of flea dirt, especially after a pet bath or washing the bedding, is a sure sign that the flea infestation is expanding.
Flea dirt is a mixture of blood and flea waste material. One flea’s trash is another flea’s treasure. The waste of the adult flea is nutritious food for the wormlike flea larvae. When fleas hatch out of the egg as larvae, they hunt for this flea dirt and eat it along with hair and dead skin cells. This enables them to grow and mature to the next stage of the flea development.
Flea dirt resembles black pepper flakes and often reappears after being removed and cleaned. A flea comb will reveal flea dirt in your pet’s fur and on their skin. The best way to confirm flea dirt is to rub some suspected flea dirt in a white cloth or rag that has been wet with hot water. The hot water will redissolve some of the flea dirt and if it is flea dirt you will see red blood staining on the white cloth. In extreme cases, you will also notice this while bathing your pet. The water will turn reddish from the redissolving blood in the flea dirt. If you find flea dirt on your pet or around your home, fleas are present and active. Regular combing and bathing your pet, in addition to a flea prevention medication, will remove the irritating flea dirt and the biting nuisance fleas.
How Long Do Flea Bites Last?
How long the redness and itchy irritation from a flea bite lasts depends upon several factors. First of all, some people are simply more sensitive/allergic to the flea bite. If you are particularly sensitive to flea saliva, your bite wounds will be more severe and take additional time to heal. In addition, by making the effort to reduce the itch, you may increase the speed of which the flea bites heal. Applying healing salves to the bites can decrease the itch which allows the body to heal. Aloe vera gel, calendula gel, calamine lotion, or hydrocortisone cream can help to heal the discomfort of flea bites. However, be careful putting chemicals on your already irritated skin. Bug repellent and other chemical sprays may exacerbate the inflammation. When in doubt, contact your doctor or dermatologist for treatment options. Incessantly scratching flea bites can lead to secondary infection and pus-filled blisters. If this happens, the repair and healing of your skin will take more time.
How long flea bites take to heal may also depend upon the level of infestation. If you notice and treat fleas early, you will likely sustain fewer bites. There is some evidence that suggests that the more often you are bitten, the worse your reaction becomes. In other words, allowing fleas to bite you (and your pet) over a prolonged period of time, you may have progressively more severe reactions to the bites. If an infestation is minor and quickly treated, and you’ve experienced a minimal reaction to the bites, most people heal from flea bites in 3-7 days.
If you are experiencing itchy bites in bed but find no signs of bed bugs, fleas might be the culprit. Flea bites can cause similar symptoms and discomfort. To address flea bites, wash the affected area, use antiseptic, apply an ice pack to reduce itching, avoid scratching the bites, consider using lotions to alleviate the itch, and consult a pharmacist for antihistamines if needed. If the bites become infected or show signs of pus, it is crucial to contact your doctor promptly. It’s important to note that treating flea bites addresses the symptoms but does not solve the underlying infestation. To fully eradicate the problem, extermination methods must be employed alongside bite treatment to ensure the complete elimination of fleas.
Flea Bites on Kids
Children are susceptible to flea bites as they cuddle with the dog or cat or play outdoors in shady sandy areas. Many adorable pictures are posted online of the family dog co-sleeping with their baby. Sometimes children curl up in the dog bed with Fido and sometimes, the dog jumps onto the child’s bed. All of this love can lead to fleas jumping off of the family dog and onto the child.
A rash or welt on a child often looks more pronounced than on an adult. Children have delicate skin and their immune systems may not be fully developed. Unless a severe allergy exists, flea bites on children are rarely medically serious. However, flea bites itch like a burning fire. It is folly to expect a child to be able to curb the intense need to scratch these bite marks. Apply soothing anti-itch creams to alleviate the irritation and cover the bites if necessary. Do everything within your power to prevent these bites from becoming infected.
If there is no family pet and no one else in the household is getting bit, investigate where these bites are coming from. Check your child’s favorite outdoor play areas. If you have a sandbox, check it for fleas, if they like to dig outdoors in a shady area, check it for fleas. Anywhere that they spend time may be suspect. Sometimes, a babysitter’s dog or cat may be the source of the flea bite.
Flea Bites On Dogs And Cats
If you notice your dog or cat scratching and biting at himself, check him carefully for signs of fleas. Flea bites leave a small raised red dot on your pet’s skin, but they can be difficult to see because of all the hair on your pet. Unfortunately, dogs and cats can not be reasoned with, we therefore can not convince them to not scratch these flea bites. Further evidence of a flea infestation is flea dirt, which is the fecal matter of adult fleas. Incessant scratching, live fleas jumping about, and visible flea dirt on their skin alerts you that your pet is suffering from a flea infestation.
As with humans, some dogs are simply more sensitive to the allergens in the flea saliva and therefore develop more redness and irritation after a flea bite. More severe flea bite symptoms include biting and chewing at their skin, hair loss, scabs, and overall red inflamed skin.
The most effective flea treatments can only be obtained from your veterinarian. Fleas are showing resistance to many of the common pet medications that have been thrown at them over the years. Besides not effectively killing fleas, some of these pesticides can be irritating to people and pets. When skin is already inflamed, flea treatments should be gentle on the pet and effective against fleas.
In addition to speaking to your vet about a prescription flea medication, take remedial measures immediately. Aggressive cleaning of the areas your pet frequents can immediately bring comfort and relief to your pet.
- Wash and dry all pet bedding on high heat.
- Vacuum and/or steam the couch, chairs, or other places where your pet rests. Use vacuum attachments to reach deep into the crevices and padding of furniture.
- Vacuum or wash all carpets and rugs in the house. Use the crevice attachments to suck up adult fleas, eggs, larvae, and pupae from difficult to access areas such as where the baseboard meets the carpet.
- Continue to vacuum these areas daily to kill eggs, larvae, and adults. Don’t forget to empty your vacuum canister into the outside trash!!
- Wash and dry human bedding if pets access the beds.
To fully remedy a flea infestation, expect frequent vacuuming and laundry, prescription flea medication for your pet, and possibly a professional pest control home treatment. Because of the flea life cycle, often, flea pest control treatments require at least 2 applications. Perseverance and meticulous attention to detail will rid your home and your pet of fleas.
Identifying and treating flea bites on pets involves several steps to ensure effective relief for your furry friend. First and foremost, it is crucial to seek advice from a veterinarian before initiating any treatment. One recommended method for treating flea bites is to bathe your pet using specially formulated shampoos designed to combat fleas. When administering care, keep in mind that cold water can help reduce inflammation caused by flea bites, while warm or hot water may worsen itching. Should these initial treatments prove ineffective, it is advisable to consult your veterinarian for further guidance. They may suggest the use of steroid creams and antihistamines, which can be prescribed to help alleviate your pet’s symptoms. By following these steps and seeking professional advice, you can effectively identify and treat flea bites on your beloved animal companion.
Allergic Reactions to Flea Bites
The small red itchy bump that develops after a flea bite is a result of an allergic reaction to the saliva of the flea. The degree or severity of the allergy determines how severe the reaction. Every person’s immune response to a flea bite is unique and may even change over time with repeated exposure. Just as every person’s reaction is unique, your pet may have a more severe reaction due to an allergy to flea bites. The reaction to flea bites is easier to see in humans rather than on pets because humans have less hair on their skin. Humans and pets with a severe allergy to flea bites are said to suffer from flea allergy dermatitis or FAD.
Human Allergic Reaction to Flea Bites
A more severe allergic reaction to flea bites will manifest itself in varying degrees. With time and repeated exposure to flea bites, a person’s allergic reaction may change. In addition to the small red itchy pustule at the site of the flea puncture, generalized redness, hives, or welts on the skin may appear. These bubbles on the skin will likely be intensely uncomfortable and itchy. An individual suffering from FAD may experience an itchy sensation over their entire body rather than confined to the area of the flea bite. Sometimes these itchy wheals or hives develop into scaly skin or hardening of the skin. In some cases the underlying skin may become discolored. Hypersensitive individuals can be tested by an allergist to confirm the sensitivity to flea bites. Your doctor may be able to prescribe medications that alleviate the immediate discomfort and help to minimize your body’s reaction to flea bites.
As fleas infiltrate the carpets, couches, and crevices of your home, they leave behind abundant flea feces and particles of exoskeletons. Fleas may also bite and cause symptoms of a flea bite which are often itchy and may need treatment with antihistamine ointment. Fleas may also bite and cause symptoms of a flea bite which are often itchy and may need treatment with antihistamine ointment. As people contact or inhale these substances, some people develop allergies to them. This can cause allergic reactions similar to asthma in affected individuals. Regular and detailed cleaning with a HEPA filter vacuum can greatly reduce these allergens around your home. By working closely with your immunologist, veterinarian, and Pest Control Professional, fleas and their bites can be controlled.
Pet’s Allergic Reaction to Flea Bites or FAD
FAD, or Flea Allergy Dermatitis, is a serious consequence of flea bites. In affected dogs and cats FAD can be terribly disruptive and painful. Scratching and biting can lead to difficult to control infections and hair loss. To diagnose FAD in a pet, veterinarians look for live fleas or evidence of fleas, such as flea dirt. The flea triangle, which is down the middle of the back, down the base of the tail, and the hind legs are most likely to be harboring fleas, flea dirt, and bite marks and other skin irritations caused by fleas. In general, areas that the animal can not easily groom are the most likely to contain fleas.
Excessive scratching, licking, and biting at their body should alert you to check for fleas. Extremely red and irritated skin is common and eventually the large patches of hair will fall out. Secondary infections from rampant scratching can occur.
Cats may develop a unique immune response from flea bites. In cats, flea bitten areas may develop a rash with a crusty puss filled overlay. As you know from watching cat videos online, cats’ bodies can be highly sensitive and reactive to stimuli. Some cats will react to flea bites in a physical manner with odd behaviors such as sudden frantic movements, twitching, and running as if they are being chased. Scratching the bite is also common as the bites are usually itchy and may need treatment. In cats, a hypersensitivity to flea bites may present as an ulcer on the cat’s lip, around the bite, called a rodent ulcer or a feline indolent ulcer. This could be one of the symptoms of a flea bite that cat owners need to be aware of. These ulcers are often caused by some immune response, whether it be a food allergy or a flea allergy. If flea bite sensitivity is the cause for these lip ulcers, effective flea control will alleviate the ulcer.
Flea Bites, But I Have No Pets
Moving into a new home brings the promise of a new beginning, many laughs, and much love shared with friends and family. However, sometimes moving into a new home brings bug bites from insects unknown and itchy sleepless nights. In almost all situations where fleas are an indoor problem, there is a family pet, hence it’s crucial to treat the pet to get rid of fleas. However, in rare situations, fleas are seen jumping around and biting you and you do not have a family pet.
To understand this situation, the flea life cycle comes into play. Above, we briefly discussed the life cycle and learned that the flea life cycle may range from taking 2 weeks to 2 years. Why this span? In cold temperatures, the larval phase can last for up to 200 days. Flea larvae, which look like worms or maggots, eat the feces, shed exoskeletons of the adult fleas, hair, and skin cells. If conditions are not ideal for them to developmentally move on, they can survive as larvae on these scraps for quite a while.
When they are ready, the flea larvae spin a cocoon like wrap and envelop themselves as they pupate. Fleas can suspend or pause their development in the pupal phase if they detect there is no food available. Flea pupae can remain protected inside their cocoon for approximately 1 year, possibly longer. During this time, fleas like this are nearly invincible. The cocoon has a protective waxy coating which makes it nearly impenetrable to pest control treatments.
If a house is abandoned or sold with fleas in the pupal phase buried deep within the carpets, the fleas will not emerge as biting adults until someone else moves in. The dormant flea pupae will remain safely concealed in its cocoon until it senses the availability of a blood meal. When the new owner steps on the carpets and moves within the home, the vibrations, heat, and exhaled carbon dioxide will cause these adult fleas to leave the safety of the cocoon and seek a blood meal. These newly emerged adult fleas require a blood meal within 24 hours, but an established adult flea can live a few weeks without a host.
While puzzling at first glance, households without a family pet, can certainly struggle with a flea infestation. With no pets present the humans are voraciously attacked. These infestations, if allowed to become severe, are sometimes more difficult to eradicate. Often the first and most effective flea treatment is treating the pet, but in these cases, there is no pet to treat. Homeowners must rely on aggressive vacuuming, steaming, and laundering in addition to professional flea control treatments to eradicate the fleas from your home.
The other common reason for fleas when you have no pets is that uninvited guests moved in. You are correct that you have no pets…… but you do have animals in or under your home. This is often the case when a pet hasn’t recently left the premises. It is often a rodent, racoon, or other wildlife infestation that is going unnoticed in the attic or crawlspace. Unfortunately, racoons and rodents do not cooperate and let you treat them with flea medicine…… These unwelcome visitors must be removed before you will achieve effective flea control in the home. In addition, wildlife infestations are often causing a great deal of other damages to the home too. If you are in this situation, please call a professional such as Nextgen Pest Solutions as soon as possible.
Do Fleas Carry Diseases?
Yes, fleas carry a plethora of diseases. There are over 2,500 species of fleas in the world, but only a few of these species are known to transmit diseases to humans. Of these species, each flea specializes in a few unique diseases. Most disease transmission occurs when fleas feed on an infected host and then move on to feed on humans. Transmission can also occur when flea feces, or flea dirt, is scratched into an open wound. The quintessential example of a flea borne disease is the Black Death or Bubonic Plague of the Middle Ages. This ghastly disease, which killed approximately 25 million people or 1/3 of the Earth’s population, was spread by the Oriental Rat Flea.
By far the most common flea that we encounter in the United States is the cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis. Although the cat flea is capable of spreading the plague bacteria, it does so very inefficiently. However, the cat flea is known to transmit cat scratch disease and flea-borne typhus.
Cat scratch disease is transferred to humans by the scratch of a cat that has the bacteria Bartonella henselae. This bacterium is given to the cat from an infected flea. A person infected with cat scratch disease may exhibit enlarged lymph nodes, fever, and a scab or pustule at the site of the scratch. This bacterium is most common in kittens, and cat scratch disease is most common in children. Most cases of cat scratch disease are mild and do not require extensive testing or medical treatment. Serious complications are extremely rare and generally occur in people with weakened immune systems.
Flea-borne (murine) typhus is also spread to humans by the common cat flea. This disease is rare in the United States but may be found sporadically in southern California, Hawaii, and parts of Texas. Flea-borne typhus is caused by the bacteria Rickettsia typhi. The fecal matter of adult fleas is often called flea dirt. This flea dirt can accumulate in the fur of our pets, and in our bedding, couches, and recliners, if our furry friends frequent them. If infected flea dirt/feces is rubbed into an open wound the bacteria may be passed to a person. It may also be transmitted by inhaling flea dirt or inadvertently rubbing it in your eyes. Severe illness is rare from flea-borne typhus and it is treatable with antibiotics. Symptoms include:
- Fever and Chills
- Body Aches and Pains
- Loss of Appetite, Nausea, Vomiting
- Cough
- Rash
As both cat scratch fever and flea-borne (murine) typhus have symptoms common to many other diseases, recognizing and diagnosing these ailments can be difficult for medical professionals. If you know that you were bit by a flea prior to exhibiting any symptoms, inform your doctor of such. Testing for these diseases can take time but your doctor may choose to begin treatment prior to confirmation of the diagnosis.
The dog flea, tenocephalides canis, is a known vector of Dipylidium, a tapeworm of cats and dogs. Recall that despite the confusing name, our canine family members are most commonly afflicted by the cat flea not the dog flea. Children in particular are most susceptible to being infected with this tapeworm. Transmission occurs when we accidentally swallow a flea infected with the tapeworm larvae. As children cuddle with and love on their pet, especially if they sleep together, they may injeingest an infected flea. This tape worm is easily treated and the treatment is generally well tolerated.
The 2 remaining flea species in the United States, the ground squirrel flea, Oropsylla montana and the Oriental rat flea, Xenopsylla cheopisare carriers of the bacteria that causes the plague. The bacteria that causes the plague is called Yersinia pestis. Humans can contract this disease by being bitten by one of these fleas. In the United States, plague is mostly limited to rural areas in the western United States. With prompt treatment, plague is easily treatable with modern antibiotics. However, without treatment, the plague can be fatal.
In the developed world with high quality medical care, flea bites are rarely a serious medical concern. Some people may experience severe redness, itchiness, and hives from insect bites such as fleas, but in most cases a flea bite to your ankle serves as a reminder to put the medication on your dog or cat. Keeping current with flea spot treatments can prevent flea infestations in your home and on your pet.
If you notice that your pet’s current flea medication seems to be ineffective, talk to your vet about an alternative active ingredient. There are many newer products on the market that fleas have not yet developed a resistance to. However, most are only available from a veterinarian. To prevent a full-blown flea infestation, act quickly when you first spot a jumping flea. Working in conjunction with your veterinarian, your professionals at Nextgen Pest Solutions have protocols to treat flea hiding places and make sure they do not come back.